
human APRIL, MBP/His-Tag
€340.00
Price excl. shipping costs excl. VAT. For more information, see our shipping policy
SKU: P2020-167 trenzyme
Description
A proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL), also known as tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 13 (TNFSF13), plays a key role in promoting the survival, proliferation and differentiation of B cells, thereby contributing to the maintenance of humoral immunity. Moreover, APRIL induces class-switch recombination to immunoglobulin A (IgA), which is crucial for the generation of mucosal immunity and defense against pathogens at mucosal surfaces. Dysregulation of APRIL may result in excessive plasma cell activation and antibody production, leading to autoimmune pathology or the development of plasma cell malignancies, such as multiple myeloma. Thus, targeting APRIL has become an attractive therapeutic strategy.

Overview
-
Product Name: human APRIL, MBP/His-Tag
-
Catalog No.: P2020-167
-
RefSeq Links: HGNC:11928; NX_O75888; NP_003799.1; NM_003808.3; PDBe 1xu1; UniProt: O75888
- Synonyms: Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 13, TNFSF13, A proliferation-inducing ligand, TNF- and APOL-related leukocyte expressed ligand 2 (TALL-2), TALL2, TNF-related death ligand 1 (TRDL-1), CD256, ZTNF2
Sequence Information
- Species: Homo sapiens
- Tags: MBP/His-tag, N-terminal
-
Sequence without tags (AA 105-250):
MAVLTQKQKKQHSVLHLVPINATSKDDSDVTEVMWQPALRRGRGLQAQGYGVRIQDAGVY
LLYSQVLFQDVTFTMGQVVSREGQGRQETLFRCIRSMPSHPDRAYNSCYSAGVFHLHQGD
ILSVIIPRARAKLNLSPHGTFLGFVKL
Product Information
-
Expression Host: HEK293
-
Formulation: PBS; pH 7.4
- Format: Liquid, stored and shipped at -80° C
-
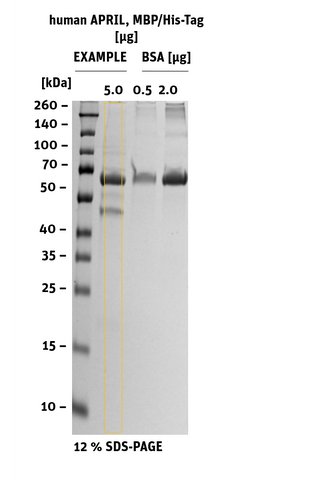
Purity: > 70 % as determined by SDS-PAGE
- Application: no recommendation
Background Information
A proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL), also referred to as tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 13 (TNFSF13), belongs to the TNF superfamily of cytokines and is produced by various immune cells, including dendritic cells, monocytes, macrophages and activated T cells. It plays a pivotal role in promoting the survival, proliferation and differentiation of B cells and thus, represents a key cytokine contributing to the maintenance of humoral immunity. As homotrimer, APRIL exerts its effects through interactions with two receptors: B cell maturation antigen (BCMA) and transmembrane activator and calcium modulator and cyclophilin ligand interactor (TACI), both of which are predominantly expressed on B cells. Along with other factors, such as the B cell activating factor (BAFF), APRIL mediates the differentiation of B cells into plasma cells committed to produce antibodies. Plasma cells express high levels of BCMA, making them highly responsive to APRIL. APRIL signaling via BCMA provides a crucial survival signal for plasma cells, promoting their long-term survival in the bone marrow niche. In the absence of T cell help, APRIL is able to induce the synthesis of the enzyme activation-induced deaminase (AID) in antigen-activated B cells by activation of TACI. AID is the key enzyme required for isotype switching. Predominantly, APRIL induces isotype switching to immunoglobulin A (IgA), promoting mucosal immunity and defense against pathogens at mucosal surfaces. Interestingly, APRIL and BAFF also assemble as heteromers, predominantly in patients with autoimmune diseases. These heteromers are characterized by distinct receptor-binding specificities and activities. Aberrant APRIL expression or signaling may contribute to excessive plasma cell activation and antibody production, resulting in the development of several autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis, all of which have elevated APRIL serum levels in common. Moreover, dysregulation of APRIL participates in the pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy, a chronic autoimmune kidney disease characterized by the deposition of IgA antibodies in the glomeruli of the kidneys, leading to inflammation and progressive renal damage. Furthermore, APRIL has been implicated in the development and progression of plasma cell malignancies, such as multiple myeloma, as it promotes the proliferation, survival and drug resistance of malignant plasma cells within the bone marrow microenvironment. Targeting APRIL signaling pathways holds promise as a therapeutic strategy for treating autoimmune diseases as well as plasma cell malignancies.
|
SDS-PAGE/Coll. Coomassie |
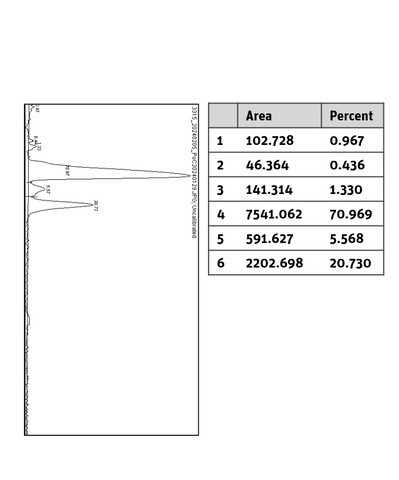
Histogram of marked lane in gel picture |
 |
 |



